Search in this section
Preface
The topic data security is now more important than ever before. Most of us are almost constantly online be it with a laptop, smartphone or tablet. We retrieve our mails everywhere, chat with friends or shop online. Unfortunately, the least attention is paid to whether the data is also protected, that is to say the data is encrypted when being transferred, while you are logged in to your bank or interacting with a merchant who processes your credit card data. It is now easier than ever before for companies to provide their customers with the right security.
With an SSL certificate implemented on the website, any data exchange is completely encrypted which means that data can not be read by anyone else. An EV certificate also strengthens the trust of the customer or prospective customer by directly displaying that the company has been verified and actually exists. For the site operator, there is another advantage: Google now evaluates all websites with Always-On-SSL better than those with only one certificate in a sub-area on the website or if no certificate is used at all.
Certificate Types
Generally speaking, there are three types of SSL certificates. These differ in the type of verification and the information visible to the user / end user within the certificate. A website secured with an SSL certificate can be recognized by the lock displayed in the browser URL bar. The certificate details can be viewed by clicking on the lock and then on further information / details / certificate. Usually this is a three to four click process.
Certificates with extended validation (EV)
The most trustworthy certificates for websites are the certificates with extended validation (EV). Prior to issuing the certificates, the relevant applicant and his / her data are examined by the relevant issuing authority.
First, it is checked whether the applicant is the owner of the domain. In addition, the company is audited on the basis of the commercial register entry. Lastly a telephone verification takes place. This means that the company's telephone number is searched for in a public directory and a phone call is made to the number found there. The verification phone call takes place in several steps:
- The first call is made to the personnel department to clarify whether the employee registered for the order is actually working for the company.
- Subsequently, a call is made to a supervisor to check whether the contact person has the authorization for this order.
- Finally, a call is made to the actual contact person to confirm the order.
These verification phone calls usually take place in English and during normal business hours.
Notice
Before placing an order it is important that the corresponding entries in the Whois, Company Register or the telephone book are present.
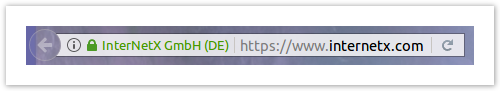
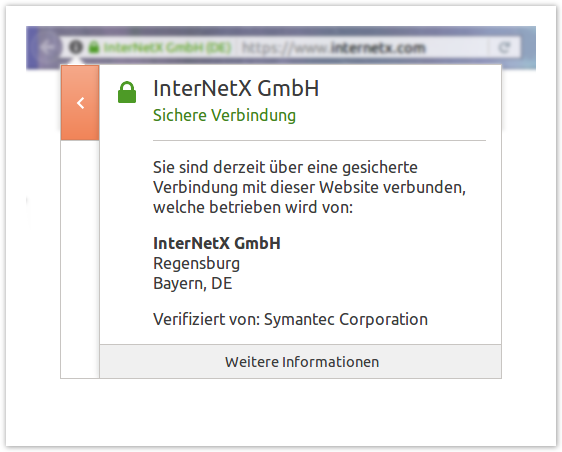
The extended validation and the restrictions during the issuance make it easier for the customer to recognize that a certificate is active and who the operator of the site is. In contrast to the two other types of certificate types, not only the small green lock is displayed, but also the operator of the page is shown.
By clicking on the green area in the URL bar, the customer / user receives further information about the operator of the website.
The advantages of this type of certificate are therefore obvious: visitors to the site are immediately informed of the SSL encryption and the company that operates the site. For more information, the customer can only click one or two times instead of clicking through hidden details.
Company-validated certificate (OV)
Der nächste Zertifikatstyp ist das unternehmensvalidierte Zertifikat (OV). Bei diesem Zertifikat entspricht der Validierungsprozess weitesgehend dem der EV Zertifikate. Auch hier ist bereits vor der Bestellung wichtig, dass entsprechende Einträge in Whois, Handelsregister oder dem Telefonbuch abgeglichen werden. Sobald das Zertifikat ausgestellt wurde, erscheint neben der Domain auch das Unternehmen in den Zertifikatsdetails. Das gibt den Usern/Kunden die Sicherheit, dass es sich hier um eine existierende Firma handelt. In der Adresszeile des Browsers erscheint nur das grüne Schloss!
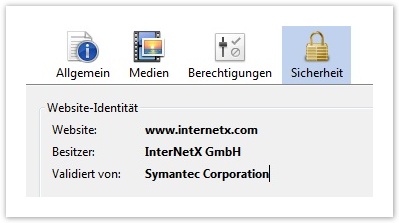
The next certificate type is the company-validated certificate (OV). For this certificate, the validation process largely corresponds to that of the EV certificates. Again, it is important to make sure that the corresponding entries in Whois, Company Register or the telephone book are set before ordering. As soon as the certificate has been issued, the company name will appear next to the domain in the certificate details. This gives the users / customers the assurance that this is an existing company. In the browser's URL bar, only the green lock will appear!
Domain-validated certificates (DV)
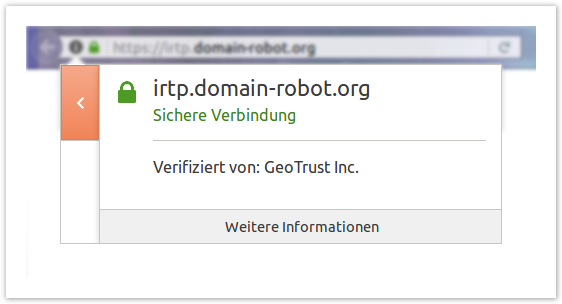
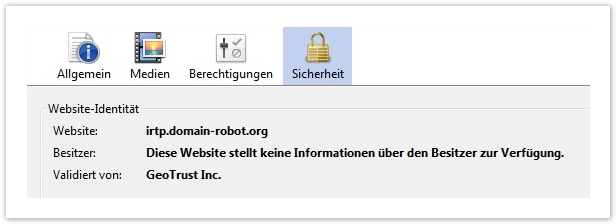
The lowest amount of security is offered by domain-validated certificates (DV). The validation is accomplished with a confirmation e-mail which is sent to a particular recipient address. In this e-mail you will find a link to confirm the order. When the confirmation is made, the certificate is issued within a few minutes. Since no further check takes place with this certificate type, there is no information on the website owner within the certificate, but the common name is listed.
Notice
All certificates can be ordered quickly and easily via the SSL-Manager.